跟我一起学习drgn(2)---核心概念

本文介绍 drgn 中的一些核心概念.
Programs
A program being debugged is represented by an instance of the drgn.Program class. The drgn CLI is initialized with a Program named prog; unless you are using the drgn library directly, this is usually the only Program you will need.
program 表示正在被调试的程序实例, 其ptyhon class 是drgn.Program. 通常情况下, 在 drgn 运行时, 只有一个单独的 program 实例. 我们可以在控制台(交互模式)或者ptyhon文件(脚本模式)中使用 prog 对其进行访问.
drgn.Program的type()、variable()、constant()和function()方法可以用来访问被调试程序中的类型、变量、常量和函数. 注意, 需要这些符号是被导出的
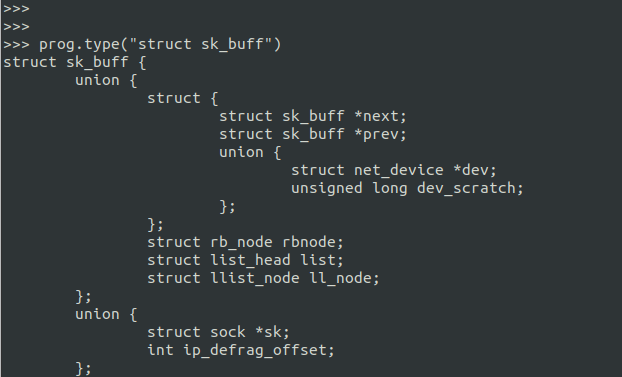
比如当我们想知道当前内核结构struct sk_buff 的定义时, 可以用 type() 方法
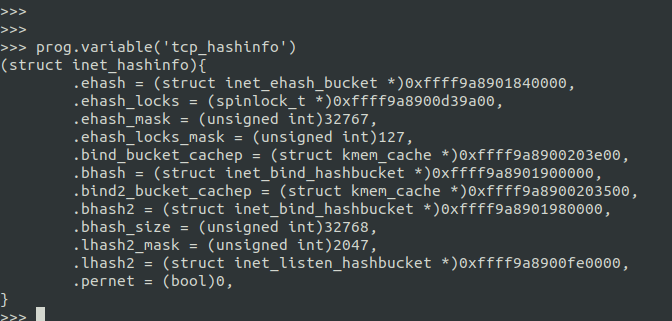
当我们向知道当前内核中变量tcp_hashinfo的值时, 可以使用variable()方法
我们可以使用[]操作符号来简化variable()、constant()和function(). 比如上面的例子使用prog['tcp_hashinfo']也能得出相同的结果.
Objects
上文提到的 variable、constant、funtion 在 drgn 中 都被称为 objects, 其 python class 是 drgn.Object
drgn 的一个特点是, 你可以在脚本里通过(.)操作符像访问内核源代码的一样访问这些 objects.
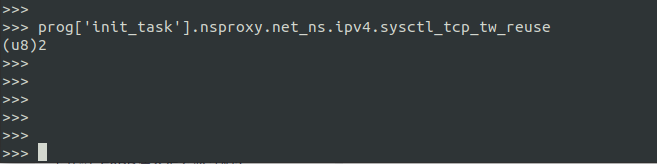
比如像下面这个例子, 我们从 init_task 中一级一级找到 sysctl 参数
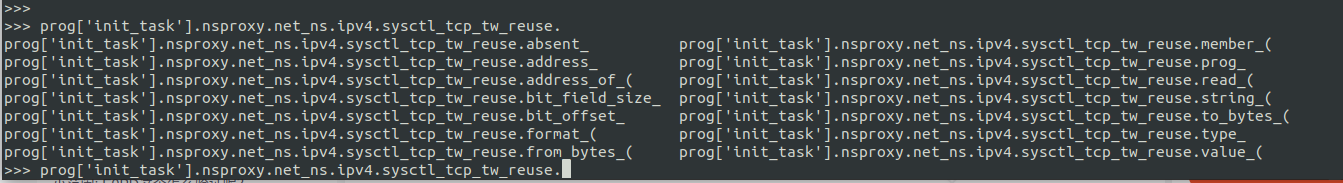
每个drgn.Object还有一些 attributes, 这些属性以下划线(_)为后缀, 在 drgn 交互模式下, 我们通过 Tab 可以看到这些 attributes
Helpers
前面的例子中,我们已经展示了如何使用 drgn 显示内核中的一些简单数据结构的值, 但是内核中还有一些访问起来比较复杂的结构, 比如链表.
因此, drgn 提前准备了一些通用的 Helpers 函数, 使用者可以直接调用它们. 其中, 链表读取访问就是其中一类.
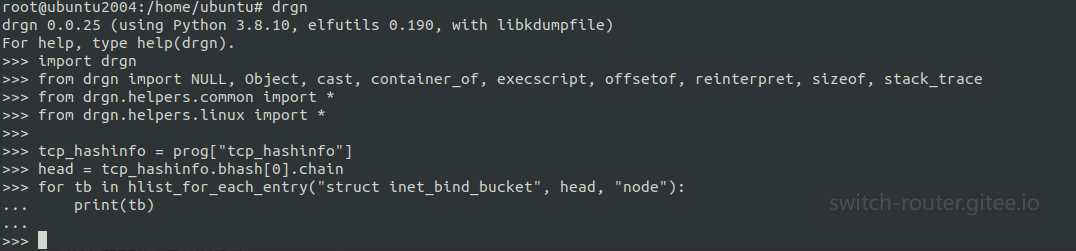
举个例子, hlist_for_each_entry就是其中的一个函数
def hlist_for_each_entry(
type: Union[str, Type], head: Object, member: str
) -> Iterator[Object]:
"""
Iterate over all of the entries in a hash list.
:param type: Entry type.
:param head: ``struct hlist_head *``
:param member: Name of list node member in entry type.
:return: Iterator of ``type *`` objects.
"""
type = head.prog_.type(type)
for pos in hlist_for_each(head):
yield container_of(pos, type, member)
我们可以使用这个函数访问内核代码中的 hlist
类似的 Helpers 函数还有很多, 具体可参考 内核相关Helpers